NTS-pico3 Device monitoring: Różnice pomiędzy wersjami
| (Nie pokazano 10 pośrednich wersji utworzonych przez tego samego użytkownika) | |||
| Linia 8: | Linia 8: | ||
[root@rbmtx ~]# gpsmon</code> | [root@rbmtx ~]# gpsmon</code> | ||
[[File:NTS-pico3_monitoringgnss.png|600px| | [[File:NTS-pico3_monitoringgnss.png|600px|frameless|class=tlt-border]] | ||
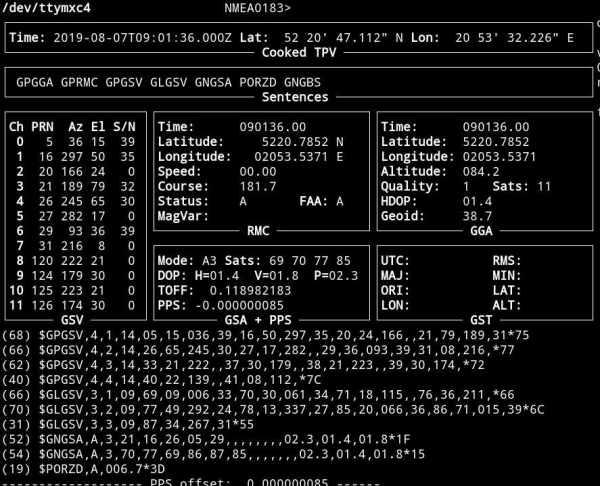
This screen is the tool to monitor GNSS (GPS & Glonass) satellite signal performance. You should be able to receive signals from at least not less than 4 satellites. Well done installation mostly let view 10-20 GNSS satellites in view. It takes approx. 5-10 minutes since power on to get minimum #sats in view. | This screen is the tool to monitor GNSS (GPS & Glonass) satellite signal performance. You should be able to receive signals from at least not less than 4 satellites. Well done installation mostly let view 10-20 GNSS satellites in view. It takes approx. 5-10 minutes since power on to get minimum #sats in view. | ||
| Linia 15: | Linia 15: | ||
For Linux/Unix and Mac OSX please use BASH std. terminal. | For Linux/Unix and Mac OSX please use BASH std. terminal. | ||
For Microsoft Windows there are various of 3rd party SSH software suppliers. One of the most popular one is free available [https://www.putty.org/ putty]</blockquote> | For Microsoft Windows there are various of 3rd party SSH software suppliers. One of the most popular one is free available [https://www.putty.org/ putty]</blockquote> | ||
===Parameter description=== | |||
'''1. Time:''' This parameter shows the current time obtained from the GPS signal. It is displayed in the format of hours:minutes:seconds (HH:MM:SS).<br> | |||
'''2. Lat (Latitude) and Lon (Longitude):''' These parameters display the current latitude and longitude, determining the GPS receiver's location on the Earth's surface. Latitude is expressed in degrees (°), minutes ('), and seconds (") in the north or south direction, and longitude is expressed in degrees, minutes, and seconds in the east or west direction.<br> | |||
'''3. Altitude:''' This parameter shows the current altitude above sea level (in meters or feet) based on GPS signal data.<br> | |||
'''4. Speed:''' This parameter displays the current speed in units such as kilometers per hour (km/h) or knots (kt). It represents the receiver's movement speed.<br> | |||
'''5. Course:''' Course is the direction in which the GPS receiver is moving. It is given in degrees (°) and indicates the geographic direction of the receiver's movement.<br> | |||
'''6. Satellites:''' This parameter informs about the number and quality of visible GPS satellites. It may display a list of satellites in view and their status, including Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) and other information. The Signal-to-Noise Ratio is a measure of the strength of the signal from each satellite, which can help in assessing the quality of the GPS fix. Higher S/N values generally indicate a stronger signal.<br> | |||
'''7. Mode:''' The GPS mode indicates whether the GPS receiver is operating in 2D (two-dimensional) or 3D (three-dimensional) mode. The 2D mode means the receiver has access to only latitude, longitude, and time, while 3D mode adds altitude information.<br> | |||
'''8. Fix:''' The "fix" information indicates the quality of GPS data. A fix can be "No fix" (no solution), "2D fix" (two-dimensional solution), or "3D fix" (three-dimensional solution).<br> | |||
'''9. HDOP (Horizontal Dilution of Precision):''' HDOP is a parameter that informs about the horizontal accuracy of GPS measurements. A lower HDOP value typically indicates higher accuracy.<br> | |||
'''10. VDOP (Vertical Dilution of Precision):''' VDOP is a parameter that informs about the vertical accuracy of GPS measurements. A lower VDOP value indicates higher accuracy in the vertical dimension.<br> | |||
'''''Note:'' Empty Frame on middle right:''' If this frame remains empty on your screen, it means that no data for that particular category is currently available. gpsmon displays data as it receives it from the GPS receiver. If there's no relevant information for that frame at a given moment, it will appear empty. | |||
'''Note:''' clockAccuracy is set according to selected time source by ntpd and GNSS PPS offset (if "GPS" selected). So clockAccuracy is changing and set to 0xFE (unknown) both in short GNSS holdover and for other time sources like RTC holdover and NTP. | |||
===Adding GGA frames=== | |||
To enable the GGA frame on every NTS-Pico3 startup, you should add command to ''User -> files -> Startup script'' section: | |||
<code>#!/bin/bash<br> | |||
echo -ne "\$PERDCFG,NMEAOUT,GGA,1*54\r\n" > /dev/ttymxc4</code> | |||
The reason for disabling the GGA frame is the default configuration setting of the GNSS module. | |||
==Monitoring NTP on-line== | ==Monitoring NTP on-line== | ||
| Linia 26: | Linia 52: | ||
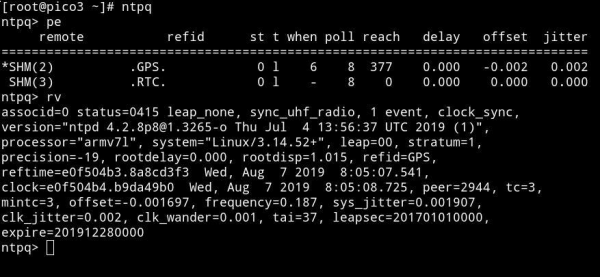
You can use full spectrum of std. NTP monitoring tools incl. '''ntpq''' and '''ntpdc''' to trace and monitor Network Time Protocol. For more information please refer to [https://www.ntp.org www.ntp.org] | You can use full spectrum of std. NTP monitoring tools incl. '''ntpq''' and '''ntpdc''' to trace and monitor Network Time Protocol. For more information please refer to [https://www.ntp.org www.ntp.org] | ||
[[File:NTS-pico3_monitoringntp.png|600px| | [[File:NTS-pico3_monitoringntp.png|600px|frameless|class=tlt-border]] | ||
===Synchronizing Microsoft Windows clock=== | ===Synchronizing Microsoft Windows clock=== | ||
| Linia 32: | Linia 58: | ||
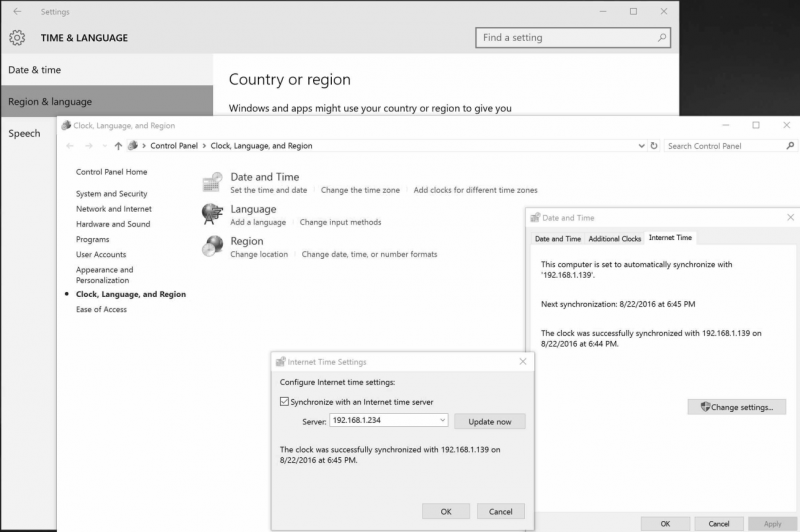
You can simply synchronize any version of Microsoft Windows system by selecting “Time from Internet” and providing '''NTS-pico3''' IPv4 address. Below is an example for Windows 10 system. | You can simply synchronize any version of Microsoft Windows system by selecting “Time from Internet” and providing '''NTS-pico3''' IPv4 address. Below is an example for Windows 10 system. | ||
[[File:NTS-pico3_synchrwindows.png|800px| | [[File:NTS-pico3_synchrwindows.png|800px|frameless|class=tlt-border]] | ||
===Synchronizing Linux & Mac OSX clock=== | ===Synchronizing Linux & Mac OSX clock=== | ||
Both Linux and OSX systems includes built-in NTP protocol. You can simply modify ntp.conf file by providing your '''NTS-pico3''' IPv4 address, however we recommend to use similar Microsoft Windows high level OS Time & Date operations. | Both Linux and OSX systems includes built-in NTP protocol. You can simply modify ntp.conf file by providing your '''NTS-pico3''' IPv4 address, however we recommend to use similar Microsoft Windows high level OS Time & Date operations. | ||
Aktualna wersja na dzień 15:15, 19 kwi 2024
Monitoring GNSS satellite signals ON-LINE
To monitor GNSS signals SSH communication must be enabled first. Please execute the following commands from terminal:
ssh root@192.168.1.234 -p 65535
root@192.168.1.139's password: 12345
[root@rbmtx ~]# TERM=vt220
[root@rbmtx ~]# gpsmon
This screen is the tool to monitor GNSS (GPS & Glonass) satellite signal performance. You should be able to receive signals from at least not less than 4 satellites. Well done installation mostly let view 10-20 GNSS satellites in view. It takes approx. 5-10 minutes since power on to get minimum #sats in view.
Recommendation!
For Linux/Unix and Mac OSX please use BASH std. terminal.
For Microsoft Windows there are various of 3rd party SSH software suppliers. One of the most popular one is free available putty
Parameter description
1. Time: This parameter shows the current time obtained from the GPS signal. It is displayed in the format of hours:minutes:seconds (HH:MM:SS).
2. Lat (Latitude) and Lon (Longitude): These parameters display the current latitude and longitude, determining the GPS receiver's location on the Earth's surface. Latitude is expressed in degrees (°), minutes ('), and seconds (") in the north or south direction, and longitude is expressed in degrees, minutes, and seconds in the east or west direction.
3. Altitude: This parameter shows the current altitude above sea level (in meters or feet) based on GPS signal data.
4. Speed: This parameter displays the current speed in units such as kilometers per hour (km/h) or knots (kt). It represents the receiver's movement speed.
5. Course: Course is the direction in which the GPS receiver is moving. It is given in degrees (°) and indicates the geographic direction of the receiver's movement.
6. Satellites: This parameter informs about the number and quality of visible GPS satellites. It may display a list of satellites in view and their status, including Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) and other information. The Signal-to-Noise Ratio is a measure of the strength of the signal from each satellite, which can help in assessing the quality of the GPS fix. Higher S/N values generally indicate a stronger signal.
7. Mode: The GPS mode indicates whether the GPS receiver is operating in 2D (two-dimensional) or 3D (three-dimensional) mode. The 2D mode means the receiver has access to only latitude, longitude, and time, while 3D mode adds altitude information.
8. Fix: The "fix" information indicates the quality of GPS data. A fix can be "No fix" (no solution), "2D fix" (two-dimensional solution), or "3D fix" (three-dimensional solution).
9. HDOP (Horizontal Dilution of Precision): HDOP is a parameter that informs about the horizontal accuracy of GPS measurements. A lower HDOP value typically indicates higher accuracy.
10. VDOP (Vertical Dilution of Precision): VDOP is a parameter that informs about the vertical accuracy of GPS measurements. A lower VDOP value indicates higher accuracy in the vertical dimension.
Note: Empty Frame on middle right: If this frame remains empty on your screen, it means that no data for that particular category is currently available. gpsmon displays data as it receives it from the GPS receiver. If there's no relevant information for that frame at a given moment, it will appear empty.
Note: clockAccuracy is set according to selected time source by ntpd and GNSS PPS offset (if "GPS" selected). So clockAccuracy is changing and set to 0xFE (unknown) both in short GNSS holdover and for other time sources like RTC holdover and NTP.
Adding GGA frames
To enable the GGA frame on every NTS-Pico3 startup, you should add command to User -> files -> Startup script section:
#!/bin/bash
echo -ne "\$PERDCFG,NMEAOUT,GGA,1*54\r\n" > /dev/ttymxc4
The reason for disabling the GGA frame is the default configuration setting of the GNSS module.
Monitoring NTP on-line
To monitor NTP, SSH communication must be enabled first. Please execute the following commands from terminal:
ssh root@192.168.1.234 -p 65535
root@192.168.1.139's password: 12345
[root@rbmtx ~]# ntpq
You can use full spectrum of std. NTP monitoring tools incl. ntpq and ntpdc to trace and monitor Network Time Protocol. For more information please refer to www.ntp.org
Synchronizing Microsoft Windows clock
You can simply synchronize any version of Microsoft Windows system by selecting “Time from Internet” and providing NTS-pico3 IPv4 address. Below is an example for Windows 10 system.
Synchronizing Linux & Mac OSX clock
Both Linux and OSX systems includes built-in NTP protocol. You can simply modify ntp.conf file by providing your NTS-pico3 IPv4 address, however we recommend to use similar Microsoft Windows high level OS Time & Date operations.