NTS-pico3 Device monitoring
Monitoring GNSS satellite signals ON-LINE
To monitor GNSS signals SSH communication must be enabled first. Please execute the following commands from terminal:
ssh root@192.168.1.234 -p 65535
root@192.168.1.139's password: 12345
[root@rbmtx ~]# TERM=vt220
[root@rbmtx ~]# gpsmon
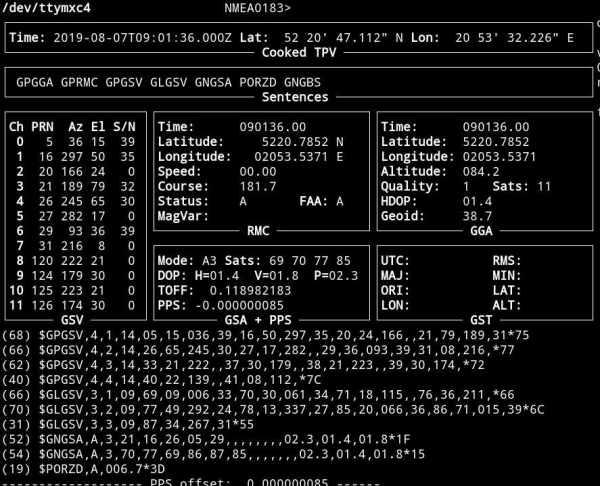
This screen is the tool to monitor GNSS (GPS & Glonass) satellite signal performance. You should be able to receive signals from at least not less than 4 satellites. Well done installation mostly let view 10-20 GNSS satellites in view. It takes approx. 5-10 minutes since power on to get minimum #sats in view.
Recommendation!
For Linux/Unix and Mac OSX please use BASH std. terminal.
For Microsoft Windows there are various of 3rd party SSH software suppliers. One of the most popular one is free available putty
Monitoring NTP on-line
To monitor NTP, SSH communication must be enabled first. Please execute the following commands from terminal:
ssh root@192.168.1.234 -p 65535
root@192.168.1.139's password: 12345
[root@rbmtx ~]# ntpq
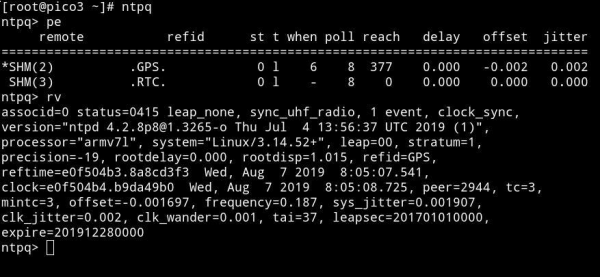
You can use full spectrum of std. NTP monitoring tools incl. ntpq and ntpdc to trace and monitor Network Time Protocol. For more information please refer to www.ntp.org
Synchronizing Microsoft Windows clock
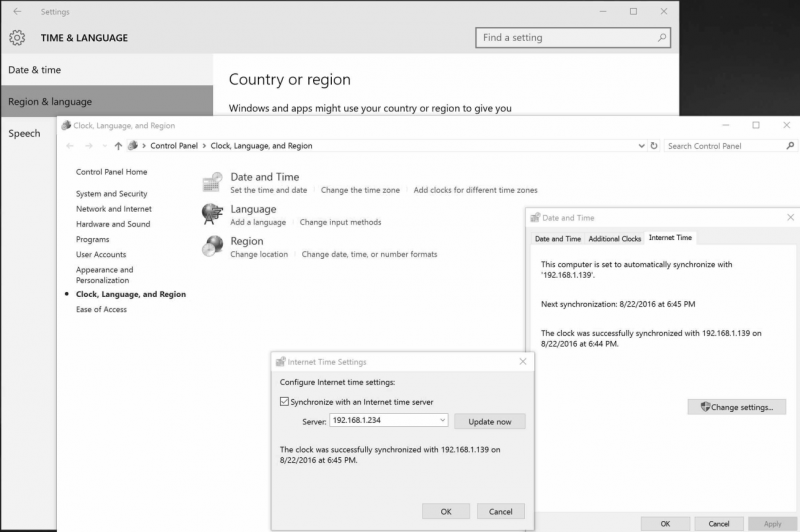
You can simply synchronize any version of Microsoft Windows system by selecting “Time from Internet” and providing NTS-pico3 IPv4 address. Below is an example for Windows 10 system.
Synchronizing Linux & Mac OSX clock
Both Linux and OSX systems includes built-in NTP protocol. You can simply modify ntp.conf file by providing your NTS-pico3 IPv4 address, however we recommend to use similar Microsoft Windows high level OS Time & Date operations.